Agriculture has been a cornerstone of human civilization for thousands of years. Advances in farm automation technology have enabled the production of enough food to support a growing global population. However, with the world population projected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, meeting future food demands will require another big boost in agricultural productivity and efficiency. Farm automation, through the use of robots, artificial intelligence, sensors, and other technologies, offers a way to sustainably increase yields while conserving resources. This article will explore what farm automation entails and how smart technologies are transforming agriculture.
What is Farm Automation?
Farm automation refers to the use of advanced technologies to automate and optimize various farming operations. Also known as precision agriculture or smart farming, the goal is to boost productivity while reducing waste and environmental impact. Farm automation involves using technologies like:
- Autonomous tractors and farming equipment powered by GPS and computer vision.
- Drones equipped with cameras and sensors for field surveying and crop monitoring.
- Internet of Things (IoT) sensors placed throughout fields to collect real-time data on soil conditions, crop health, weather, etc.
- Artificial intelligence and analytics software to interpret data and support decision-making.
- Automated irrigation systems that adjust watering based on sensor data.
- Robots and machines for tasks like planting seeds, weeding, harvesting, pruning, and sorting crops.
By automating routine physical tasks and leveraging data to optimize operations, farm automation removes some of the guesswork from farming. It empowers farmers to increase yields, reduce costs, and make their operations more efficient, profitable, and sustainable.
Key Technologies Enabling Farm Automation
A range of advanced technologies are making automated, data-driven farming possible. Here are some of the most important:
Autonomous Tractors and Farm Equipment

Tractors and other farm equipment equipped with GPS, sensors, and computer vision technology can accurately navigate fields and perform tasks with minimal human intervention. John Deere and other manufacturers already offer tractors that can steer themselves and follow predetermined routes using GPS coordinates. Sensors enable tractors to detect and avoid obstacles in their path. In the future, fully driverless equipment will be able to completely automate key tasks like tilling, planting, spraying, and harvesting crops.
Drones

Agricultural drones equipped with multispectral cameras can survey crop fields from the sky to create detailed maps of the entire farm. These images reveal variations in factors like plant health and soil conditions so farmers can take targeted action. Drones can also apply fertilizer, pesticides or water only to areas in need, reducing waste. Startups like DroneDeploy and Sentera provide drone technology tailored for agriculture uses.
Crop Sensors
Sensors installed throughout crop fields can continuously monitor key variables like soil moisture, nutrient levels, leaf wetness, and crop stress. Connecting these to the internet allows remote monitoring and data collection to inform irrigation, fertilizer, and pest management decisions. For example, CropX provides a combination of in-ground sensors and cloud-based analytics to optimize watering and fertilizer application.
Robotics
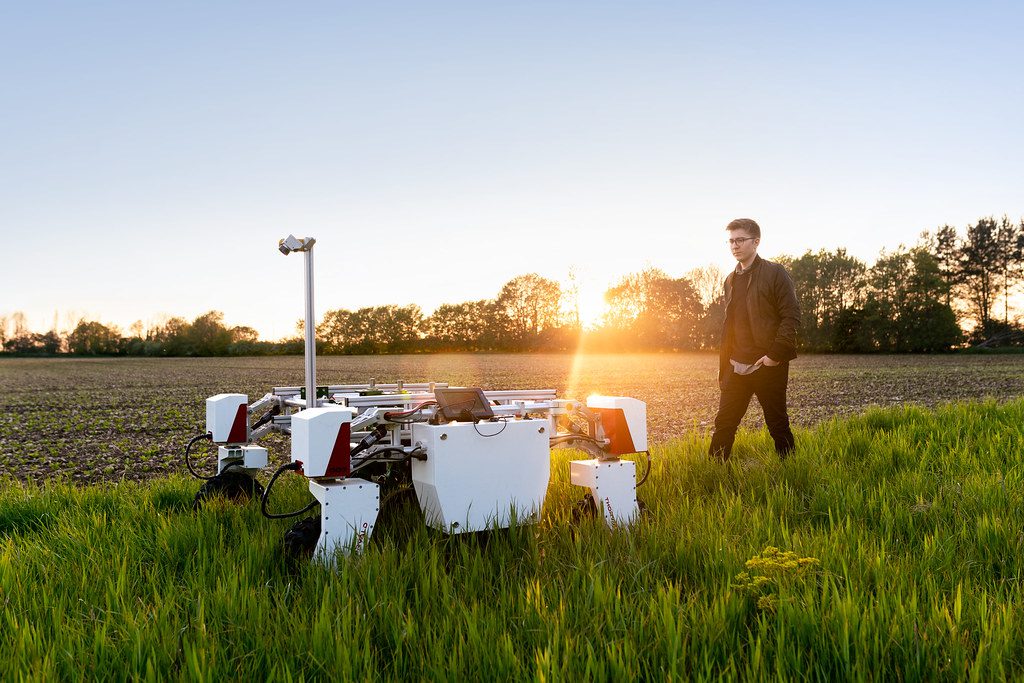

Agricultural robots can take over tedious and back-breaking jobs traditionally performed manually. Startups are developing robotic systems for tasks like precision planting and seeding, mechanical weeding, picking fruits and vegetables from plants, and pruning vines and trees. Companies like Abundant Robotics and Iron Ox are creating robotics tailored for specialty crops.
Farm Management Software
Software platforms like Granular, Agricolus, and Cropio aggregate data collected by field sensors, equipment, and drones into a single dashboard that farmers can monitor from any device. These provide analytics and recommendations on where and when to plant, spray, fertilize, harvest, and more. Farm management systems enable farmers to detect patterns and optimize their operations.
Benefits of Farm Automation
Adopting smart farming technologies delivers numerous benefits for agricultural operations including:
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
Automating manual tasks like planting, crop spraying, and harvesting enables farmers to be more efficient. Less time spent on labor means lower operational costs. Robots and sensors also collect data that helps improve decision making and optimize workflows to boost productivity.
Reduced Need for Manual Labor
Labor shortages have impacted agriculture, making farm automation technologies more appealing. Automated equipment and robots can take over certain physically demanding jobs traditionally performed by human workers. This saves money on labor costs while reducing risks of injuries.
Resource Conservation
Precision agriculture technologies allow for more targeted use of key inputs like water, fertilizer and pesticides. Applying water or chemicals only where and when needed, guided by crop sensor data, results in less waste. Similarly, tractors equipped with auto-steering minimize overlapping passes and fuel consumption.
Data-Driven Decision Making
The data collected through sensors, equipment, and drones provides unprecedented insights. By analyzing this, farmers can make smarter decisions about when to plant, irrigate, or apply crop treatments. Advanced analytics assists with predicting yields, detecting disease early, and planning for weather disruptions.
Waste and Loss Reduction
Monitoring tools allow farmers to catch crop stress signals early and take corrective action before losses occur. Automated picking and processing systems minimize crop damage compared to manual handling. This means higher yields and less waste due to spoilage.
Increased Farmer Profits
The efficiency gains, waste reduction, and ability to optimize operations leads to increased yields and cost savings from farm automation. This directly translates into improved profit margins for farmers who invest in agricultural technology.
Challenges Facing Adoption of Farm Automation
While farm automation offers immense potential, there are hurdles slowing more widespread adoption among farmers:
High Upfront Costs
Sensors, farming robots, and autonomous equipment require major up-front capital expenditures that may be prohibitive for small farms. Larger operations can more easily absorb these costs and benefit from economies of scale.
Technical Complexity
Implementing cutting-edge automation technologies can prove daunting for farmers without technical backgrounds. Farm workers will need training to operate new unmanned, automated systems and interpret collected data.
Resistance to Change
Some farmers are set in their ways and hesitant to fix what isn’t broken. Convincing traditional farmers to embrace disruptive technologies like AI and robotics will take education and demonstrated benefits.
Data Privacy Concerns
Sensors and equipment collecting extensive farm data raises understandable privacy concerns. Farmers want to control their data and may distrust sharing it with third parties like equipment manufacturers.
Connectivity Issues
Lack of reliable internet connectivity in rural agricultural areas can hamper the effectiveness of connected farm automation technologies dependent on real-time data.
The Future of Farm Automation
The agriculture industry is still only scratching the surface when it comes to leveraging advanced technology to automate farm operations. However, we are clearly moving towards a future of smarter, more efficient farming powered by automation. Key trends to expect include:
Continued Innovation in Robotics
Startups will continue building robots specialized for tasks like fruit picking, weed control, and autonomous seed planting and fertilizing. With costs decreasing over time, more farms will invest in robots.
AI and Predictive Analytics
Accumulated field data fed into artificial intelligence algorithms will enable betteryield predictions. AI may also help create custom dynamic treatment plans tailored to each farm’s conditions.
Adoption of Autonomous Equipment
Fully driverless tractors and farming implements will become mainstream. This autonomous equipment will be able to handle critical jobs safely with minimal oversight.
Development of Automated Vertical Farms
Indoor vertical farming facilities maximizing space via stacked layers will leverage automation to precisely control nutrients, lighting, humidity, and harvesting. These highly-productive controlled farm environments located right in cities will expand.
Expanded Drone Capabilities
Drones will progress from being aerial surveyors to multifunctional tools. Onboard manipulator arms will enable drones to perform delicate tasks like targeted spray applications, fruit picking, and sensor installation.
Increased Adoption Across Global Agriculture
While the U.S. currently leads in smart agriculture, countries across South America, Europe, Asia, and Africa will increasingly integrate automation technologies to stay competitive.
Conclusion
Farm automation presents immense opportunities to make agriculture more efficient, productive, profitable, and sustainable. Technologies like autonomous equipment, AI, drones, and robotics are transforming farming. However, change won’t happen overnight. Realizing the full possibilities will require continued technological improvements. It will also take investments in equipment and training by farmers, as well as optimism about the benefits of digital agriculture. Farm automation won’t replace farmers entirely, but rather augment and empower them. Adopting smart technologies will be key to meeting rising food demands while conserving resources. The future of farming is autonomous, data-driven and highly precise.